[3D Printing Techniques] 2024 Guide to Improving 3D Printing Tolerances - Make Your 3D Prints Meet Expectations
In the rapidly evolving world of additive manufacturing, understanding 3D printing tolerances is crucial to the success of the final product. This article highlights the importance of 3D printing tolerances and provides simple steps to test and improve print quality. Whether you're a beginner or an intermediate user, save this article to make your 3D printing more accurate and rewarding.

The tolerance of a 3D printer refers to the acceptable dimensional variation of the printed object compared to the original model. This variation is inevitably caused by a variety of factors, including the type of printer, the materials used, the part design, and the printer calibration. High-precision printers can limit this variation, typically measured in micrometers (µm) or millimeters, ensuring that the finished product is as close as possible to the intended design.
3D printing tolerances require a delicate balance. If they are too tight, the print may fail; if they are too loose, components may not fit properly. Therefore, understanding and adjusting tolerances is crucial for the success of the 3D printing process.
Why are tolerances important in 3D printing?
Understanding 3D printing tolerances is key to achieving high-quality printing. In this section, we'll explore the importance of tolerances in 3D printing, from printing accuracy to functional compatibility, to ensure your projects meet expected specifications and standards.
• Precision and accuracy
Precision refers to how close a measured value is to a standard or known value, while accuracy refers to how close multiple measurements are to each other. Both are important in 3D printing. Parts with appropriate tolerances ensure both accuracy (closeness to the original design) and precision (dimensional consistency).
• Efficiency and cost savings
Understanding and using tolerances can help you reduce print failures and the need for post-processing, thereby improving time and material efficiency and ultimately saving costs.
• Interchangeability of parts
For projects involving interchangeable parts, precise tolerances are crucial. Even minor variations in design dimensions can lead to part incompatibility, requiring additional iterations or even project failure.
• Functional parts: When printing functional parts such as gears and connectors, strict tolerances are essential to ensure the performance and fit of the parts.
• Surface quality : Tolerances also affect the surface quality, texture, and appearance of printed objects. Adjusting tolerances can help reduce printing errors such as warping, streaking, ghosting, or layer shift.
• Material properties : Different printing materials have different effects on tolerances. For example, some materials shrink when cooled, which should be considered when designing tolerances. Understanding the behavior of various materials is crucial for achieving the desired tolerances.
How to test the tolerances of a 3D printer?
This step not only reveals the printer's precision but also provides a benchmark for improvement. Whether you're solving a problem or simply looking to improve print quality, learning how to effectively test the tolerances of a 3D printer is an essential skill for every 3D printing enthusiast. Let's explore the methods and tools needed to perform these tests.
• Print calibration model


(Source: Bambu Lab Maker World )
Begin your 3D printing tolerance testing by printing a specially designed calibration model. This model should test various dimensions and features, such as thin walls, holes, and overhangs. You can easily find such models online or create your own using CAD software.
• Measurement Results <br> After printing the calibration model, use precision measuring tools, such as calipers or micrometers, to measure the dimensions of the printed parts. Compare these data with the original design dimensions to determine deviations, helping you understand the printer's tolerances.
• Test different print settings .<br>Change the printer settings and test its performance under different conditions. This may include adjusting layer height, print speed, nozzle temperature, and fill percentage. By doing so, you can find the optimal settings to improve printer tolerances.
• Testing different materials
3D printing materials have different properties that can significantly affect tolerances. Test your printer using different materials, such as PLA, ABS, and PETG, to understand how material selection impacts printer tolerances.
• Testing Overhangs and Support Structures <br> The ability to print overhangs and generate support structures is crucial for complex 3D models. Test the printer's performance in these areas by printing models with varying degrees of overhang and different types of support structures.
• Repeated testing to ensure consistency <br> To ensure accuracy and reliability, multiple tests are performed using the same calibration model. Repeated testing helps verify the consistency of the printer's performance under identical conditions.
How to improve 3D printing tolerances?
Having explored how to test 3D printer tolerances, let's now delve into effective strategies for improving tolerances. This section will guide you through practical techniques to achieve higher accuracy in 3D printing.
• Maintain and calibrate the printer
Perhaps the most important way to achieve maximum printing accuracy and stay within tolerances is to calibrate the machine. A poorly calibrated printer can result in parts that are not straight, are incorrectly sized, and do not fit together. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the print bed, lubricating moving parts, and tightening screws, can significantly improve tolerances in 3D printing. Furthermore, ensuring the print bed is level and calibrating the extruder and other printer parts helps improve accuracy.
• Optimized slicing settings
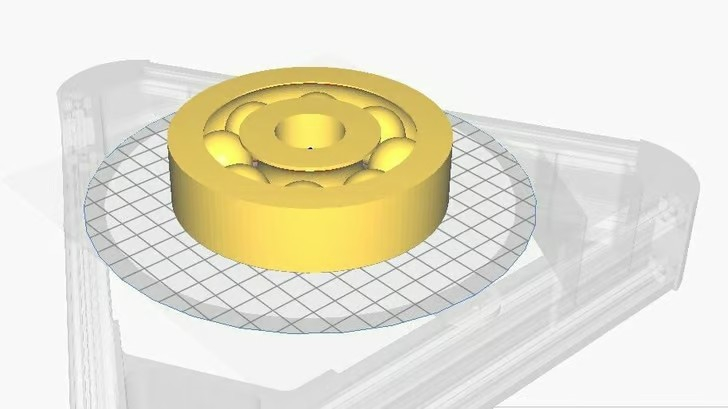
(Source: Paul via MathCodePrint )
Adjusting slice settings is a necessary step to achieve better tolerances. Adjust parameters such as layer height, print speed, and nozzle temperature to find the optimal balance between print quality and speed.
• Environmental control
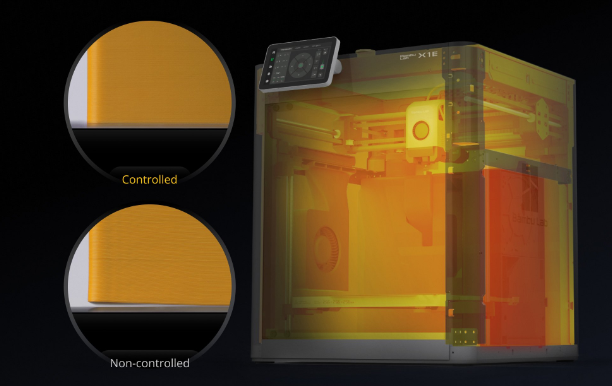
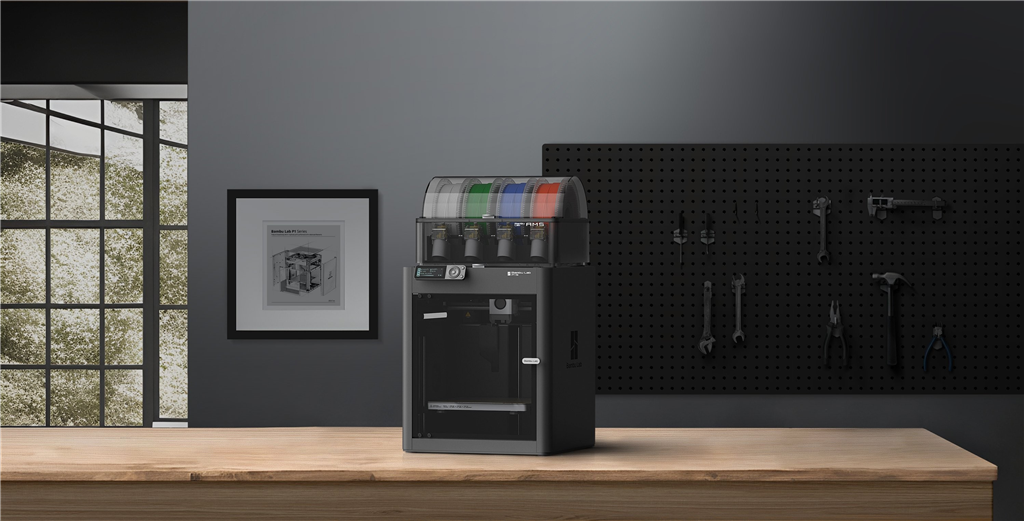
The Bambu Lab X1E can actively heat and regulate the chamber temperature, improving print quality and tolerances (Source: Bambu Lab Official ).
Temperature and humidity in the printing environment significantly affect printing tolerances. Maintaining a stable and controlled environment leads to more consistent and accurate printing. Consider using an enclosure to stabilize temperature and reduce airflow.
• Use high-quality cables
• Adjusting model tolerances during the design process
In most applications, the joint between two parts has a specific function.
For example, consider a circular shaft with a diameter of 50 mm, which should fit into a circular hole with a diameter of 50 mm. In reality, there are three options for how these two parts should be combined:
.png)
• Clearance fit <br> The shaft diameter is significantly smaller than the bore diameter, at 49.8 mm and 50.2 mm respectively. In this case, the shaft will easily slide in and out of the bore and rotate within it.
• Interference Fit <br> The diameter of the shaft is the same as or slightly wider than the diameter of the hole, such as 50.2 mm and 49.8 mm respectively. Without significant force, the shaft will not fit into the hole. Once it does, it may not be able to be removed without damaging the parts. This type of fit is widely used when high concentricity and mutual movement are required (e.g., connecting a shaft to a bearing).
• Transition Fit<br> The shaft diameter is only slightly smaller than the bore diameter, at 49.9 mm and 50.0 mm respectively. The shaft will be installed in the bore with minimal pressure and maintain relative concentricity. Alternatively, the shaft diameter may be slightly larger than the bore diameter and require slightly more pressure (but not as much as an interference fit).
In reality, each fit type spans a range of allowed combinations. The dimensions given above are merely examples. Several international standards (such as ISO tolerances) exist for correctly selecting the fit and corresponding design, but they will not be discussed in this article.
• Post-processing
Even with all calibrations, proper design, and special slicing configurations, parts may still exceed tolerances. In such cases, they need to be aligned with post-processing. There is no shame in accepting the need for post-processing of parts. Even when using extremely precise CNC machining centers costing hundreds of thousands of dollars to fit and conform to specifications, some post-processing is necessary; techniques such as grinding, filing, or drilling can help achieve better fit and functionality.
• Consider upgrading your printer
Hardware upgrades can significantly improve printing tolerances. This may include replacing the original nozzles with high-precision nozzles, upgrading to a more accurate heated bed leveling system, or investing in a printer with a more robust frame.
Make good use of AI to save too many 3D printing tests and steps
AI-powered smart 3D printers significantly improve ease of operation, printing accuracy, and troubleshooting capabilities by incorporating artificial intelligence technology, making 3D printing more automated and intelligent. In contrast, traditional 3D printers require more manual operation and specialized knowledge, making them suitable for experienced users or less complex printing tasks.
| Traditional 3D printers | AI-powered Smart 3D Printer |
|
1. Manual adjustment and calibration Manual leveling of the print bed and calibration of the extruder are required. Setting and adjusting printing parameters (such as temperature, speed, and layer height) requires a certain level of expertise and experience. |
1. Automated adjustment and calibration It features an automatic leveling function to ensure the print bed remains flat at all times. It can automatically calibrate the extruder and other critical components, significantly reducing the need for manual operation by the user. |
|
2. Limited monitoring and control Control is limited to basic interfaces and software. Monitoring during the printing process relies primarily on the user's visual observation, making precise monitoring and adjustment difficult. |
2. Intelligent monitoring and control Equipped with an AI camera and sensors, it can monitor the printing process in real time and make adjustments based on the data. It also features remote control capabilities, allowing users to operate it via a mobile application or web interface. |
|
3. Troubleshooting relies on user experience. When printing errors occur (such as warping, stringing, or layer shifting), users need to rely on experience to troubleshoot and resolve the problems. |
3. Intelligent troubleshooting AI can analyze problems during the printing process, such as layer misalignment, stringing, and curling, and automatically make adjustments or prompt the user to perform corresponding operations. It provides real-time feedback on the printing process to ensure high-quality printing . |
|
4. Limited equipment upgrade options; manual hardware upgrades are required. |
4. Diverse hardware upgrade options <br>More high-precision components and modules to choose from |
|
5. The operation is relatively complex , requiring considerable professional knowledge and experience. |
5. User-friendly operation ; suitable for all types of users, including beginners and professionals. |
Bambu Lab X1 Carbon Combo 3D Printer
The Bambu Lab X1 Carbon Combo 3D printer revolutionizes additive manufacturing, achieving printing speeds of up to 500 mm/s. With a precision of 0.1 mm and built-in AI camera monitoring, every print is exceptionally accurate and efficient. It features a lidar and AI system that automatically detects the print quality of the first layer , sending alerts to your phone if any abnormalities are detected. Automatic leveling ensures precise alignment and easy assembly for every print , laying the foundation for improved tolerances in 3D printing.
Topzhu Bambu Lab X1E 3D Printer

The X1E 3D printer is designed for industrial use and also features AI algorithms that utilize LiDAR and computer vision to detect defects and surface errors in the first layer . It is equipped with a chamber temperature control system (up to 60°C or 140°F) , a printing speed of up to 500 mm/s, an extrusion flow rate of 32 mm³/s , and an accuracy of 0.1 mm. Compared to the X1C, it can print on a wider range of filaments, especially PC or ABS materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (Q&A)
• What are good tolerances for 3D printing?
Good dimensional tolerances for 3D printing are typically around 0.1 mm. Because 3D printing is an additive process, it generally exhibits larger tolerance deviations compared to subtractive techniques such as injection molding or CNC machining. Therefore, it is important to consider these potential deviations during the design phase.
What tolerances are required for 3D printed parts to fit together ?
The tolerances required for mating 3D printed parts vary depending on the desired degree of fit. For a tight fit, a clearance of 0.005 inches (approximately 0.127 mm) is typically required. For a standard fit, it is typically around 0.010 inches (approximately 0.254 mm), while for a loose fit, it should be around 0.020 inches (approximately 0.508 mm). For press fits, parts are typically produced line-to-line, meaning the shaft and hole diameters are nearly identical. In all cases, given the nature of 3D printing tolerances, testing and iterative design may be necessary to achieve the desired results.
For Bambu Lab equipment purchases, Santima offers a one-year standard warranty or enhanced warranty . For any operational inquiries, please contact Santima via email.

🔧【Standard Warranty Plan 】+$0
| Free gift with purchase |
We provide free parts and repair training methods, and ship the parts to a designated location → Customers assemble the product themselves using the parts.
👨💻【Enhanced Warranty Service Plan】+$5,580
Free shipping | Free testing |Free repair
San Di Ma will send someone to collect repair equipment free of charge. → Santima engineer performs repair → After completion, Santima dispatches a vehicle to return it.
Did you enjoy this sharing session?
Learn more about 3D printing filaments and 3D printers , or contact us for high-quality 3D printing OEM services.
Follow our fan page and stay up-to-date with the latest news:
https://www.facebook.com/3dmart.com.tw/
https://www.instagram.com/3dmart/








